Breathing is a necessary part of life. Oxygen is inhaled and carbon dioxide is exhaled. The average person takes in about 20,000 breaths a day. So where does all the atmosphere go? It doesn’t just disappear. It’s used by the body to create energy.
Air is essential for the body to create energy. The process of turning sugar into energy requires this element. When sugar and air combine, they form carbon dioxide and water. This process happens in all the cells in the body. The energy created by this reaction helps the body to function properly. You must apply more wellness tips to improve blood oxygen saturation.
Atmosphere is also important for growth and repair. New cells are created when old ones die off. These new cells need dioxygen to grow and thrive. Air also helps to heal wounds and damaged tissues.
What happens to oxygen when it’s exhaled?
When we breathe in, the air is transferred from the air into our bloodstream. The blood carries the atmosphere to all of the tissues in our body. When we breathe out, carbon dioxide is transferred from the tissues into the bloodstream. The blood carries the carbon dioxide back to the lungs, where it is exhaled.
The Air then diffuses through the alveoli and into the blood. From there, it is distributed to all of the tissues in our body. When we exhale, carbon dioxide leaves our body and is expelled through our lungs.

The human body needs a constant supply of air to survive. If the amount of air decreases in our blood, we become unconscious.
Every day, we take in dioxygen and release carbon dioxide. This is a natural process, but what happens to all the air we breathe in? Silent hypoxia is a condition where there is not enough dioxygen reaching the tissues. This can be caused by many things, such as smoking, air pollution, and altitude. In some cases, it can be deadly. Silent hypoxia is often overlooked because it doesn’t have any obvious symptoms.
It can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. If left untreated, it can lead to heart attack, stroke, or even death. One of the biggest dangers of silent hypoxia is that it can worsen COVID-19 patients. When there is less oxygen available, the virus spreads faster and causes more damage. This puts patients at risk for serious health complications and even death.
Breathing is a necessary function for all living beings, but what many people don’t know is where the oxygen goes after we breathe it in. Our lungs take in oxygen from the air and blood cells use the oxygen to break down glucose and other nutrients to create energy. The waste product of this process is carbon dioxide, which we exhale.
The amount of oxygen in the air hasn’t changed, but with an increase in pollution, there’s more carbon dioxide in the air. This means that our bodies are working harder to get the same amount of oxygen. Over time, this can lead to a decrease in the amount of oxygen that’s available to our cells, a condition called hypoxia.
How does the body use and store oxygen?
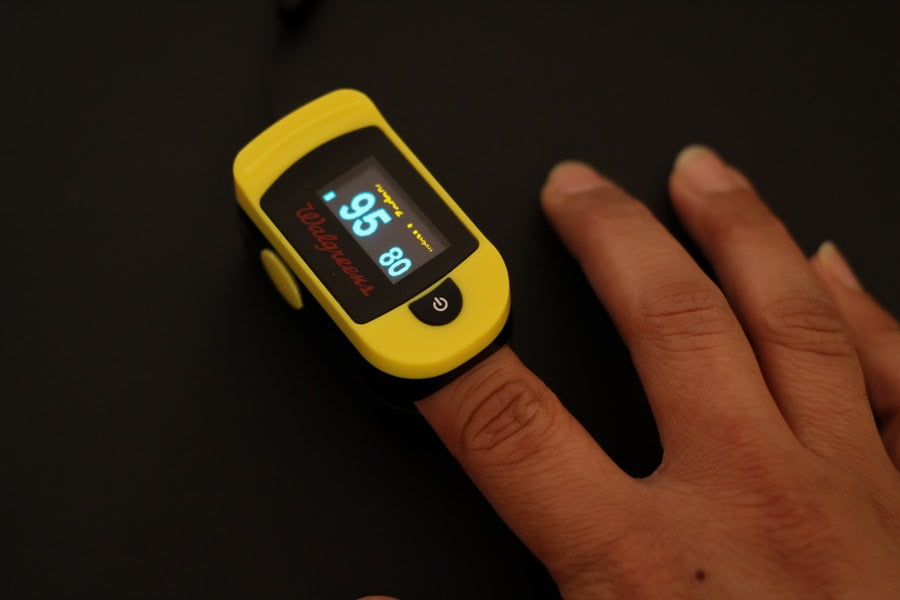
The human body requires dioxygen to survive. We breathe in air and the body uses it for energy. The lungs absorb the atmosphere and send it through the bloodstream to be used by the cells throughout the body. The blood delivers the oxygen to where it is needed most. The human body can only store a limited amount of oxygen.
Once the body has used all of the air, it needs more fresh air to breathe in. When we breathe out, we release carbon dioxide from our bodies. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is created when the cells use the air for energy.
Most of the air we breathe in is exhaled. About 21% of inhaled oxygen is retained in our blood and distributed throughout our body. The rest of the inhaled dioxygen is exhaled through our lungs.
What are the health benefits of air?
Did you know that every day we breathe in about 21,000 liters of air? And that’s not even counting the dioxygen we consume through food! So what happens to all that air? Well, a lot of it is used to break down the food we eat into glucose and other nutrients. The rest is used by our cells to create energy.
Dioxygen is also essential for cell growth and repair. In fact, without air our cells would die very quickly. That’s why it’s so important to make sure we always have plenty of this element available. Not only does it help us stay healthy, but it also helps us feel more energetic and alert. So next time you take a deep breath, be sure to thank all those little air atoms for keeping you healthy and happy!
The primary component of air is nitrogen, which makes up 78% of the atmosphere. Dioxygen accounts for 21% of the air, with argon making up the remaining 1%. The majority of air is found in the lower part of the atmosphere, while nitrogen is more evenly distributed.
4 ways to improve blood oxygen saturation level at home
- One way to improve blood air saturation level is to increase your activity level. When you are active, your body needs more air, and therefore takes in more air. This can help improve blood oxygen saturation levels.
- Another way to improve blood dioxygen saturation levels is to use a CPAP machine if you have sleep apnea. A CPAP machine helps keep your airway open while you sleep, so you can breathe easier and get more air into your bloodstream.
- You can also improve blood dioxygen saturation levels by using a humidifier when you are sick. A humidifier will help loosen mucus and make it easier for you to breathe.
- You can develop this element levels by using a nasal spray or saline rinse when you are congested. This will help clear your sinuses and make it easier for you to breathe.
Air is essential for life and is used by animals and plants to produce energy. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is harmful to both people and animals in high concentrations.